Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Mori, Masahiro; ITER Japanese Participant Team
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(1-7), p.69 - 77, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.98(Nuclear Science & Technology)The ITER Transitional Arrangements (ITA) are conducted by the International Team with supports from participant teams (PTs). The Japanese PT (JA-PT) set up in JAERI has contributed to ITA by sharing a lot of technical tasks to verify feasibilities of fabrication and quality control method in procuring ITER equipments and facilities. For examples, trial fabrications of Nb3Sn strands have been performed by JA-PT with four potential suppliers, and one of the strand which meet the ITER requirements in all key parameters have already been chosen for one of the suppliers. All strands including the other suppliers strands will be fully qualified by the end of 2005. The trial fabrications of CS jackets and material for TF coil structure are also in progress at industrial level. Fabrication of the partial mock-ups of the vacuum vessel is also ongoing. Furthermore, JA-PT has made several technical developments on NB and EC systems to improve reliability of long pulse operations. Completing these technical preparations will make it possible to finalize the specification of ITER procurements.
Nakahira, Masataka; Takeda, Nobukazu
Hozengaku, 4(4), p.47 - 52, 2006/01
The technical structural standard for ITER (International Thermonuclear Experimental Fusion Reactor) should be innovative because of their quite different features of safety and mechanical components from nuclear fission reactors, and the necessity of introducing several new fabrication and examination technologies. Recognizing the international importance of Fusion Standard, Japan and ASME has started the cooperation development of the Fusion Standard. This paper shows the special features of ITER from view points of safety, design and fabrication, and proposes approach for development of the fusion standard.
Nakahira, Masataka
JAERI-Research 2005-030, 182 Pages, 2005/09
It is difficult for Vacuum Vessel (VV) of ITER to apply a non-destructive in-service inspection (ISI) and then new safety concept is needed. Present fabrication standards are not applicable to the VV, because the access is limited to the backside of closure weld of double wall. Fabrication tolerance of VV is  5mm even the structure is huge as high as 10m. This accuracy requires a rational method on the estimation of welding deformation. In this report, an inherent safety feature of the tokamak is proved closing up a special characteristic of termination of fusion reaction due to tiny water leak. A rational concept not to require ISI without sacrificing safety is shown based on this result. A partial penetration T-welded joint is proposed to establish a rational fabrication method of double wall. Strength and susceptibility to crevice corrosion is evaluated for this joint and feasibility is confirmed. A rational method of estimation of welding deformation for large and complex structure is proposed and the efficiency is shown by comparing analysis experimental results of full-scale test.
5mm even the structure is huge as high as 10m. This accuracy requires a rational method on the estimation of welding deformation. In this report, an inherent safety feature of the tokamak is proved closing up a special characteristic of termination of fusion reaction due to tiny water leak. A rational concept not to require ISI without sacrificing safety is shown based on this result. A partial penetration T-welded joint is proposed to establish a rational fabrication method of double wall. Strength and susceptibility to crevice corrosion is evaluated for this joint and feasibility is confirmed. A rational method of estimation of welding deformation for large and complex structure is proposed and the efficiency is shown by comparing analysis experimental results of full-scale test.
Takeda, Nobukazu; Omori, Junji*; Nakahira, Masataka
JAERI-Tech 2004-068, 27 Pages, 2004/12
ITER vacuum vessel (VV) is a safety component confining radioactive materials such as tritium and activated dust. An independent VV support structure with multiple flexible plates located at the bottom of VV lower port is proposed. This independent concept has two advantages: (1) thermal load due to the temperature deference between VV and the lower temperature components such as TF coil becomes lower and (2) the other components such as TF coil is categorized as a non-safety component because of its independence from VV. Stress analyses have been performed to assess the integrity of the VV support structure using a precisely modeled VV structure. As a result, (1) the maximum displacement of the VV corresponding to the relative displacement between VV and TF coil is found to be 15 mm, much less than the current design value of 100 mm, and (2) the stresses of the whole VV system including VV support are estimated to be less than the allowable ones defined by ASME. Based on these assessments, the feasibility of the proposed independent VV support has been verified as a VV support.
Takeda, Nobukazu; Omori, Junji*; Nakahira, Masataka; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(12), p.1280 - 1286, 2004/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)ITER vacuum vessel (VV) is a safety component confining radioactive materials. An independent VV support structure located at the bottom of VV lower port is proposed as an alternative concept, which is deferent from the current reference, i.e., the VV support is directly connected to the toroidal coil (TF coil). This independent concept has two advantages comparing to the reference one: (1) thermal load becomes lower and (2) the TF coil is categorized as a non-safety component. Stress Analyses have been performed to assess the integrity of the VV support structure. As a result, (1) the maximum displacement of the VV corresponding to the relative displacement between VV and TF coil is found to be 15 mm, much less than the current design value of 100 mm, and (2) the stresses of the whole VV system including VV support are estimated to be less than the allowable ones defined by ASME, respectively. Based on these assessments, the feasibility of the proposed independent VV support has been verified as an alternative VV support.
Takatsu, Hideyuki; Sato, Kazuyoshi; Hamada, Kazuya; Nakahira, Masataka; Suzuki, Satoshi; Nakajima, Hideo; Kuroda, Toshimasa*; Nishitani, Takeo; Shikama, Tatsuo*; Shu, Wataru
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(1), p.178 - 182, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.18(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)This paper presents an overview on ITER-supporting materials research and development activities and major achievements in Japan during the period from the Co-ordinated Technical Activities to date. In view of the completed engineering design of ITER during the Engineering Design Activities period, research and development efforts since then have been focused: those for reduction of component fabrication cost; those in support of domestic preparations of a structural technical code for construction; those necessary for operation, and been extended to component-level testing rather than pure material testing. They cover materials Research and Development for in-vessel components, vacuum vessel, cryogenic steels of superconducting mgnet and diagnostics components. Major achievements in each research and development area are highlighted and their impact or implication to the design, construction and operation of ITER is presented.
Nakahira, Masataka; Shibui, Masanao*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Dai-9-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu, No.04-2, p.267 - 272, 2004/06
A small water leak can cause a plasma disruption in a tokamak-type fusion machine. This plasma disruption will induce electromagnetic (EM) force acting in the vacuum vessel that is a physical barrier of tritium and activated dust. If the VV can sustain an unstable fracture by the EM force, the structural safety will be assured and the inherent safety will be demonstrated. Therefore, a new analytical model to evaluate the through crack and leak rate of cooling water is proposed, with verification by experimental leak measurements. Based on the analysis, the critical crack length to terminate plasma in ITER is evaluated as about 2 mm. On the other hand, the critical crack length for unstable fracture is obtained as about 400 mm. It is concluded that EM forces induced by the small leak to terminate plasma will not cause unstable fracture of the VV; thus the inherent safety is demonstrated.
Nakamura, Hirofumi; Higashijima, Satoru; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Horikawa, Toyohiko*; Kubo, Hirotaka; Miya, Naoyuki; Nishi, Masataka; Konishi, Satoshi*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 70(2), p.163 - 173, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:75.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to establish the effective and conventional in-vessel tritium removal method, glow discharge methods, usually used as wall conditioning, have been applied and examined in vacuum vessel of JT-60U for tritium removal characteristics and kinetics. Release rates of all hydrogen isotopes as well as hydrocarbons from JT-60U vacuum vessel induced by Glow Discharge Cleaning (GDC) with He and H were measured. Release characteristics of hydrogen isotopes were classified into three different release processes each of which is well described by a simple exponential decay with time. It was found that H
were measured. Release characteristics of hydrogen isotopes were classified into three different release processes each of which is well described by a simple exponential decay with time. It was found that H GDC showed the superior hydrogen isotope release characteristics than the He GDC, probably because chemical processes, such as isotope exchanges assisted by the chemical sputtering process between discharged hydrogen and hydrogen isotopes plasma facing carbon tiles are enhanced by the H
GDC showed the superior hydrogen isotope release characteristics than the He GDC, probably because chemical processes, such as isotope exchanges assisted by the chemical sputtering process between discharged hydrogen and hydrogen isotopes plasma facing carbon tiles are enhanced by the H glow discharge. Based on the release kinetics observed in the present work, it is estimated that it will take several days to reduce tritium inventory in the surface area of JT-60U to a half by continuous H
glow discharge. Based on the release kinetics observed in the present work, it is estimated that it will take several days to reduce tritium inventory in the surface area of JT-60U to a half by continuous H GDC at 573 K.
GDC at 573 K.
Nakahira, Masataka
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(2), p.226 - 234, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.03(Nuclear Science & Technology)A tokamak-type fusion machine is said to have inherent safety associated with plasma shutdown. A small leak of water can terminate the plasma safely and can cause a plasma disruption which will induce electromagnetic(EM) forces in the vacuum vessel (VV). From a radiological safety view point, the VV forms the physical barrier that encloses tritium and activated dust. If the VV can sustain an unstable fracture by EM forces from a through crack to cause the leak, the structural safety will be assured and the inherent safety will be demonstrated. Therefore, a systematic approach to assure the structural safety is developed. A new analytical model to evaluate the through crack and leak is proposed, with verification by experiment. Based on the analyses, the critical crack length to terminate plasma is evaluated as about 2 mm, and the critical crack length for unstable fracture is obtained as about 400 mm. It is therefore concluded that EM forces induced by small leak to terminate plasma will not cause the unstable fracture of VV, and then the inherent safety is demonstrated.
Nakahira, Masataka
JAERI-Tech 2003-087, 28 Pages, 2003/12
A tokamak-type fusion machine has been characterized as having inherent plasma shutdown safety. An extremely small leakage of cooling water will cause a plasma disruption. This plasma disruption will induce electromagnetic forces (EM forces) acting in the vacuum vessel (VV) which forms the physical barrier enclosing tritium and activated dust. If the VV has the possibility of sustaining an unstable fracture from a penetrating crack caused by EM forces, the structural safety will be assured and the inherent safety will be demonstrated. This paper analytically assures the Leak-Before-Break (LBB) concept as applied to the VV and is based on experimental leak rate data of a through crack having a very small opening. Based on the analysis, the critical crack length to terminate plasma is evaluated as about 2 mm. On the other hand, the critical crack length for unstable fracture is obtained as about 400 mm. It is therefore concluded that EM forces induced by small leak to terminate plasma will not cause the unstable fracture of VV, and then the inherent safety is demonstrated.
Nakahira, Masataka
JAERI-Tech 2003-083, 79 Pages, 2003/11
The ITER Vacuum Vessel has a double-walled structure and cooling water is filled in between inner and outer shells. It is planned to apply T-welded joints with partial penetration at the connection between outer shell and rib. The length and gap of non-penetrated part are controlled and limited to less than 5mm and 0.5mm respectively. Although it can be considered to be low susceptibility, crevice corrosion can possibly occur, because the water is stagnant in the crevice and impurities will condense. In this report, the corrosion-crevice repassivation potential, E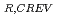 , was experimentally measured under the several density of NaCl solution, and compared to the steady-state corrosion potential in the pertinent environment, to evaluate the susceptibility. Simulated conditions are normal operating condition with water temperature of 150
, was experimentally measured under the several density of NaCl solution, and compared to the steady-state corrosion potential in the pertinent environment, to evaluate the susceptibility. Simulated conditions are normal operating condition with water temperature of 150 C, baking operation with water temperature of 200
C, baking operation with water temperature of 200 C and impurity condense by cyclic wet and dry condition.
C and impurity condense by cyclic wet and dry condition.
Kudo, Yusuke; Sakurai, Shinji; Masaki, Kei; Urata, Kazuhiro*; Sasajima, Tadayuki; Matsukawa, Makoto; Sakasai, Akira; Ishida, Shinichi
Fusion Science and Technology, 44(2), p.333 - 337, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)A modification of the JT-60U is planned to a superconducting coil tokamak (JT-60SC) to establish steady-state operation of high beta plasma during a long duration of 100 s, and to ensure the plasma applicability of ferritic steel as reduced activation materials at reactor relevant break-even class plasma. This paper describes the detailed design of vacuum vessel, which has a unique structure for the cost effective manufacturing, and also the structural analysis results for the feasibility study. Eddy current and electromagnetic load analyses in case of stationary plasma disruption is performed and the result is used as the input for the static and dynamic analyses. As a result, the dynamic analysis is necessary to avoid unpredictable inertial force.
Nakahira, Masataka
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 40(9), p.687 - 694, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.79(Nuclear Science & Technology)The ITER vacuum vessel is a double-walled torus with large-sized quadrilateral ports and is required to provide a quite high degree of vacuum for deutrium - tritium fusion reaction. The vacuum vessel is required to install after assembled with toroidal field coils. From a radiological safety aspect, the vacuum vessel is functioned as a physical barrier to enclose radioactive materials. Therefore, construction of the vacuum vessel needs application of newly developed technologies on design, fabrication and examination. The technologies include design approach by finite element analysis, and partial penetration T welded joints to join ribs to outer shell. Several issues have to be resolved for applying those technologies to the vacuum vessel. This paper describes several newly developed technologies and key issues for applying to the vacuum vessel and then their resolutions.
Tsunematsu, Toshihide; Seki, Masahiro; Tsuji, Hiroshi; Okuno, Kiyoshi; Kato, Takashi; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Hanada, Masaya; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Sakamoto, Keishi; Imai, Tsuyoshi; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 42(1), p.75 - 93, 2002/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.15(Nuclear Science & Technology)Japanese contributions to ITER Engineering Design Activity are presented, together with an introduction of the objectives and design of the ITER whose program have been carried out through the international collaboration by EU, Japan, Russian Federation and the USA. New technologies have been produced through the development, fabrication and testing of scalable models in the fields of superconducting magnet, reactor structure with vacuum vessel, high-heat-flux plasma facing component, neutral beam injector, high-power mm-wave generator and so on. As major contributions from Japan, development and testing results of a 13-T, 640-MJ, Nb Sn pulsed magnet, a 18-degree sector of vacuum vessel with a height of 15 m and a width of 9 m, CFC armors to CuCrZr cooling tube that withstood 20 MW/m
Sn pulsed magnet, a 18-degree sector of vacuum vessel with a height of 15 m and a width of 9 m, CFC armors to CuCrZr cooling tube that withstood 20 MW/m , a 31 mA/cm
, a 31 mA/cm negative ion beam source, a 1-MeV beam-accelerator, a 1-MW 170-GHz gyrotron were described.
negative ion beam source, a 1-MeV beam-accelerator, a 1-MW 170-GHz gyrotron were described.
Suzuki, Takayuki*; Usami, Saburo*; Kimura, Takae*; Koizumi, Koichi; Nakahira, Masataka; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*
Proceedings of 55th Annual Assembly of International Institute of Welding (IIW2002), 16 Pages, 2002/06
A new type of welded joint for the outer wall and rib of a double-walled vacuum vessel of a fusion reactor has been developed. The joint is manufactured by through-wall electron-beam welding (TW-EBW), in which the beam is injected from the outside of the outer wall. Static and fatigue tests are carried out on one-bead-specimens under an axial load and two-bead-specimens under a bending load. The experimental results are analytically investigated by FEM. Although this joint is partially penetrated, the net yield strength of the bead is increased by the plastic constraint due to triaxial tensile stress in the weldment. This phenomenon reduces the mean equivalent stress on the bead cross section, and the gross strength of the joint is close to that of a full thickness welded joint. The fatigue-strength reduction factor for low-cycle fatigue life is a little larger than four. The calculated fatigue-crack growth rate in the joint is conservatively calculated by using the maximum stress intensity factor of the crack and the fatigue-crack growth rate given in ASME Code Section XI.
Nakahira, Masataka; Takeda, Nobukazu; Hada, Kazuhiko; Tada, Eisuke; Miya, Kenzo*; Asada, Yasuhide*
Proceedings of 10th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 10) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2002/04
The special features of Vacuum Vessel (VV) of International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) are complicated structure and electromagnetic load. The VV is torus shaped, double-walled structure with ribs. The electromagnetic force is not uniform. Thus the rules for axisymmetric structures and loading are not effective for ITER VV. The double ミwalled structure requires one-sided welding joints with no possibility of access from the other side. Every joints between outer wall and rib and field joints are this type. The joint between outer wall and rib is special T-joint with partial penetration. To cover these special issues on ITER VV, a new code is under development. Supporting R&Ds are planned to be material tests to obtain joint efficiency and fatigue reduction factor, UT sensitivity tests, sensitivity tests on crevice corrosion and examination-free welding for application to field joints. This paper describes the special features of ITER VV from code stand point, concept of new code and R&Ds to apply the new code to ITER VV.
Nakahira, Masataka; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Kajiura, Soji*; Shibui, Masanao*; Koizumi, Koichi; Takeda, Nobukazu; Kakudate, Satoshi; Taguchi, Ko*; Oka, Kiyoshi; Obara, Kenjiro; et al.
JAERI-Tech 2002-029, 27 Pages, 2002/03
The ITER vacuum vessel (VV) R&D has progressed with the international collaborative efforts by the Japan, Russia and US Parties during the Engineering Design Activities (EDA). Fabrication and testing of a full-scale VV sector model and a port extension have yielded critical information on the fabrication and assembly technologies of the vacuum vessel, magnitude of welding distortions, dimensional accuracy and achievable tolerances during sector fabrication and field assembly. In particular, the dimensional tolerances of  3 mm for VV sector fabrication and
3 mm for VV sector fabrication and  10 mm for VV sector field assembly have been achieved and satisfied the requirements of
10 mm for VV sector field assembly have been achieved and satisfied the requirements of  5 mm and
5 mm and  20 mm, respectively. Also, the basic feasibility of the remote welding robot has been demonstrated. This report presents detailed fabrication and assembly technologies such as welding technology applicable to the thick wall without large distortion, field joint welding technology between sectors and remote welding technology through the VV R&D project.
20 mm, respectively. Also, the basic feasibility of the remote welding robot has been demonstrated. This report presents detailed fabrication and assembly technologies such as welding technology applicable to the thick wall without large distortion, field joint welding technology between sectors and remote welding technology through the VV R&D project.
Nakahira, Masataka; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; Koizumi, Koichi; Onozuka, Masanori*; Ioki, Kimihiro*
Nuclear Fusion, 41(4), p.375 - 380, 2001/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:18.28(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
*; Nakahira, Masataka; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; Tada, Eisuke; *; *
JAERI-Tech 99-026, 158 Pages, 1999/03
no abstracts in English
Koizumi, Koichi; Oka, Kiyoshi; Tada, Eisuke
Dai-8-Kai MAGDA Konfarensu Koen Rombunshu, p.252 - 255, 1999/00
no abstracts in English